
I recently came across this useful article on the FLIR website. I thought it was a great reminder for both new and experienced Thermographers on how best to capture the most accurate IR images.
Often once you have taken your image on-site and saved it there is no way of amending it or going back. Sometimes blurred images are only picked up after a survey is complete and can’t be rectified in the software. So, before we start, remember this handy little piece of information —‘FORD’.
Here’s a re-cap of the article and why you can’t afford to forget FORD
During the infrared Thermography Inspection thermal information is captured by the thermal camera. With the thermal imaging technology you can detect people and objects in total darkness and in very diverse weather conditions. Analysing the accuracy of the recorded data is a key factor, as after saving the thermal image, there is no way to change or repair the image.
To capture the highest quality image and be able to carry out a proper inspection always remember these 3 main elements:
FOcus
Range
Distance
What does FORD mean?
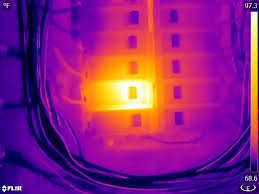
The FO is for FOcus – The focus of any image is important for both clarity & accuracy of data and for the ability to make it clear for others what is the focus of the image. You must focus carefully before storing an image, because you can’t re-focus later. Just like you do with any other camera, if you don`t focus optically the image will be blurry and will show an inaccurate temperature measurement, so your analysis will not be reliable and accurate.
Good focus=better measurement
These two images below show the difference, first one is out of focus second one is in focus:

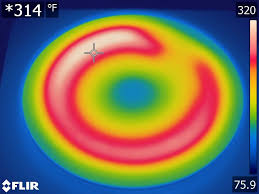
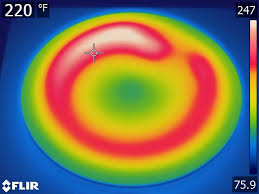
The R is for Range – This refers to the temperature range of the object, which defines how cold and hot your object will become. This could also be the coldest and hottest temperature in the scene you are viewing, but you can only measure these temperatures with a thermal camera which allows you to image the entire range at one time. As only those temperature points can be collected and measured which are within the temperature range of the thermal camera.
Most of the latest thermal cameras break the total range of the temperature measurement and cover intervals of temperature within the image without going into saturation.
The first image is made out of the correct temperature range the second one is made in the correct temperature range:
The D is for Distance – Each camera has a specified focus distance within the resolution of the image is good enough to measure the temperature accurately. Basically this means how far you are from your target when you make the image. If you are out of the focus distance the thermal camera will not be able to pick up enough pixels about the object.

A good guide is to ensure that you fill the spot circle on your measurement tool, this will ensure that you get a good accurate reading. If this is not possible, then switching to a telephoto lens (if available) is another option.
If you would like to know more about thermal imaging or you need practical experience with infrared cameras, why don`t you take a look at our range of ITC Certified Thermography Courses available for booking through PASS Training. Click HERE and get to know more about our courses.
For thermal imaging cameras and accessories, you can browse this site or contact 01642 931329 to speak to one of our qualified Thermographers.


