Please note this blog was originally published on the 12th October 2012. It was updated on the 27th May 2021 to include links to relevant Multimeter brands and company contact details. It was updated again on the 14th July 2025.
Many multimeters boast of being able to deliver true-RMS readings. However, what does this mean, and how does this data compare to RMS measurements? How are true-RMS readings taken? How is RMS data calculated? What does all this mean for you? Do you really need a true-RMS meter? Thankfully, the answers to all these questions lie in our short explanation detailing the difference between RMS and true-RMS, available below.
Quick Links
RMS & True RMS Explained
When you use a multimeter to measure an AC voltage or current, the reading on the meter is an "RMS" or "root mean square" reading. We sometimes call the RMS value the "effective value" of an AC voltage or current. By that, we mean that the RMS value of an AC voltage or current has the same effect as a DC voltage or current of the same value.
Let's consider an example. If I had a 10V DC power supply connected across a 10-ohm resistor, the power being dissipated by the resistor would be:
P = V2/R = 100/10 = 10 W
If I substitute a 10VRMS AC supply for the 10V DC supply, the power calculation would be the same, and the resistor would dissipate 10W of power. The AC voltage is, however, constantly changing, so the 10W is an average value taken over a period of time. At any particular point in time, the resistor will be dissipating more power, and at other times, less power.
Assuming that the AC voltage supplied is a pure sine wave, the peak AC voltage will be 1.414 times the RMS voltage, or 14.14 V. Taking the inverse of that, you can see that the RMS value of a sinusoidal AC voltage is 0.707 times the peak value.
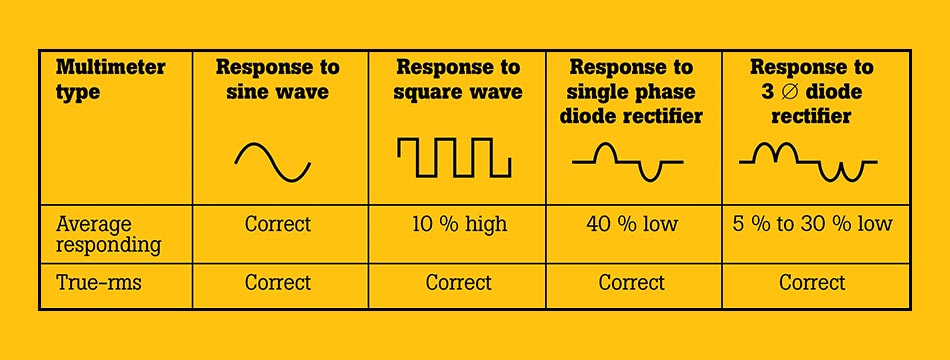
A majority of inexpensive meters use an averaging technique for determining the RMS reading of an AC voltage or current. This method provides an accurate reading when measuring an AC voltage with a sinusoidal waveform. However, if the AC voltage or current waveform you’re trying to measure is not a pure sine wave, the reading will be inaccurate, typically too low. Depending on the type of AC waveform, the reading might be up to 40% lower than it should be.
If you need to measure the voltage or current of AC signals that are not pure sine waves, such as when you’re measuring the output of adjustable speed motor controls or adjustable heating controls, then you need a “true RMS” meter. A true RMS meter works by taking the square of the instantaneous value of the input voltage or current, averaging this value over time, and then displaying the square root of this average.
The important thing to remember is that a “true RMS” meter will give you better readings. And, better readings will pay off in the long run, whether you’re making these measurements in the lab or out on the factory floor.
Further Information
We stock a range of digital multimeters that support true-RMS measurements, including models by leading brands such as by Extech, FLIR, Fluke, Kewtech, and Megger, to name a few. For more information regarding any of these instruments, please contact our Sales team on 01642 931 329 or via our online form.
In the meantime, you can browse our eclectic collection of multimeters on our website, tester.co.uk.


